How to Root Your Android Phone: The Ultimate Guide
Have you ever felt like your Android phone was holding you back? You may be tired of the pre-installed bloatware, or you may want to customize your device to the fullest extent. If so, then rooting your Android phone might be the answer you’re looking for.
Rooting, also known as jailbreaking, is the process of gaining full administrative rights on your device. This allows you to break free from the restrictions imposed by the manufacturer and unlock a world of possibilities. This means you can remove bloatware, install custom apps and software, and even change the look and feel of your phone.
There are two main ways to root an android device: using a computer or rooting without a computer. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and at the end of the article, you will learn how to root and which way to follow.
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide on how to root your Android phone using both methods. So you can ensure a smooth and successful rooting experience. We will also offer tips on how to stay safe while rooting your device.

What is Rooting?
Rooting is the process of gaining full administrative access to your device, similar to having root access on a Linux system. This means you can bypass the restrictions placed by the manufacturer and carriers to customize your device.
Rooting your Android phone gives you complete control over your device. You can remove bloatware, install custom ROMs and kernels, and overclock your processor. However, rooting also comes with risks, such as bricking your device. So before rooting an android phone or tablet, you must ensure the benefits and risks.
Benefits of Rooting
Here are some of the most essential benefits of rooting an android device:
- Enhanced performance: Rooting can improve your device’s performance by removing bloatware, optimizing system settings, and overclocking the CPU.
- Customization: Rooting opens up a world of customization options, allowing you to change themes, fonts, icons, and even the entire operating system with custom ROMs.
- Access to advanced features: Rooted devices can run apps that require root access, such as ad blockers, call recorders, and file managers with extended privileges.
- Extended Battery Life: Rooting allows you to fine-tune your device’s power consumption, potentially extending battery life.
- Rooted Apps: A vast ecosystem of rooted apps exists, offering unique features and functionalities that are not available on unrooted devices.
Risks of Rooting
While rooting offers numerous benefits, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks involved:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Rooting your device can make it more vulnerable to security attacks. This is because rooting gives apps access to the root level of your device’s operating system.
- Warranty Void: Rooting your device may void your warranty. If you have problems with your device after rooting it, the manufacturer may not help you.
- Bricking: If you root your device incorrectly, you could brick it, which means you would no longer be able to use it.
- Compatibility Issues: Some apps or features may not function properly on a rooted device.
Common Rooting Terminology
Superuser
Also known as “root” access, this is a user account with complete control over the Android OS. This allows you to make changes to the system that would typically not be possible, such as installing custom firmware, removing bloatware, and tweaking system settings.
ADB (Android Debug Bridge)
ADB is a tool used to communicate with an android device from a computer. It can be used to install apps, transfer files, and troubleshoot device issues.
Bootloader
The bootloader is a small software that starts your device before the OS loads. It is responsible for loading the kernel, which is the core of the operating system.
Fastboot
Fastboot is a mode on android that allows you to boot into the bootloader and flash firmware images. This is typically used when installing custom ROMs or rooting your device.
Custom Recovery
A custom recovery replaces the stock recovery on your android. It allows you to perform tasks such as backing up your device, restoring backups, and installing custom firmware.
Custom ROMs
A custom ROM replaces the stock firmware that comes with your android device. It’s like having a completely different phone inside your phone. It can include new features, performance improvements, and a different user interface.
Is Rooting Legal?
Rooting your Android phone is legal in most countries, but some exceptions exist. For example, rooting your device may void your warranty. It is also important to note that some root apps may be illegal in certain countries.
How to Root Your Android Phone
There are many different ways to root your Android phone. The best method for you will depend on your device and your experience level. Here are two of the most popular rooting methods. But before moving ahead, let’s look over the requirements to root your device.
Prerequisites
Before rooting your device, ensure you have the following:
- A compatible version of android device
- A USB cable
- A computer (optional)
- Backup of your device’s data
Root Android With a PC
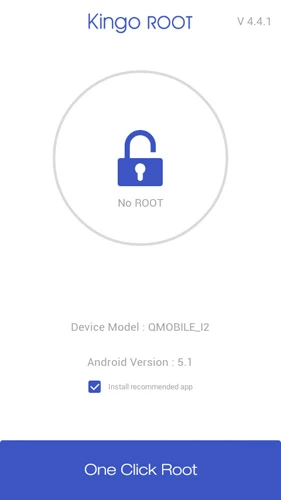
There are many different tools available for rooting android devices with a PC. Some of the most popular ones include KingoRoot, iRoot, and Framaroot. But for this tutorial, we will use Kingo Root to root android with a PC in one click.
KingoRoot is a popular and easy-to-use rooting tool that supports various devices. It has a one-click rooting feature that makes the process even simpler. Additionally, KingoRoot has a high success rate, making the rooting process successful. To root android phones and tablets with KingoRoot, follow the steps below.
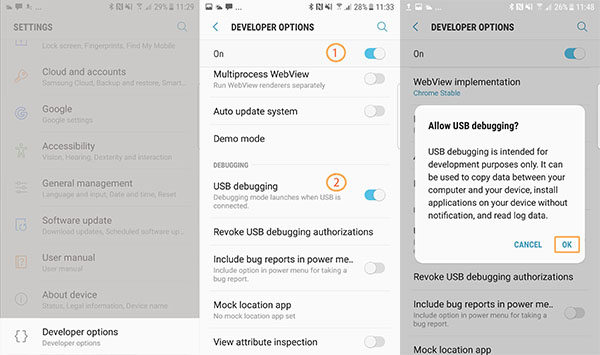
- Enable USB debugging on your device. To do this, go to Settings > About phone and tap the Build number seven times. Then, go to Settings > Developer options and enable USB debugging.

- Download and install KingRoot on your PC.
- Connect your android device to your PC using a USB cable.

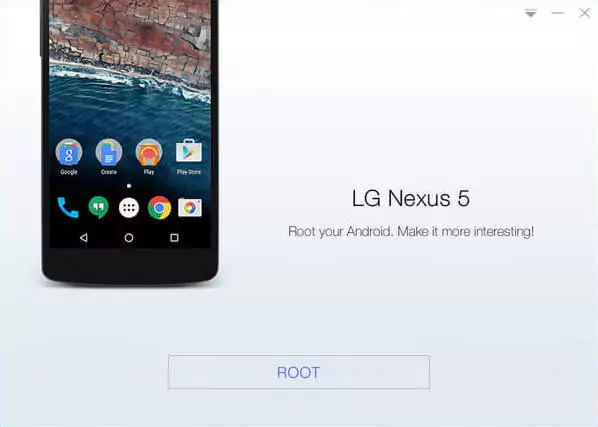
- Launch KingRoot on your PC. KingRoot will automatically detect your device and prompt you to root it.

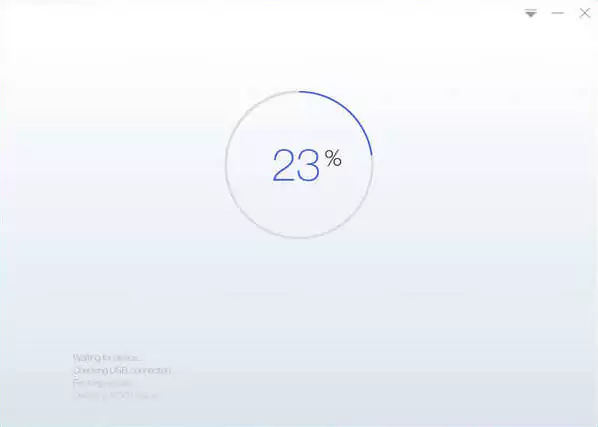
- Click the “Root” button. The rooting process will take a few minutes.

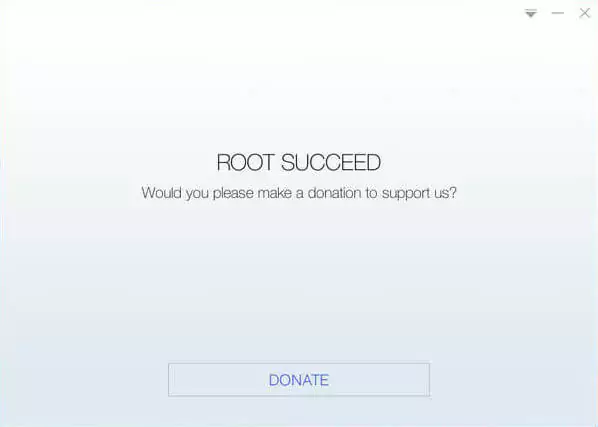
- Once the rooting process is complete, your device will reboot.

- Verify that your device is rooted. To do this, open the KingRoot app on your device and tap the “Verify Root” button.
Congratulations! You have successfully rooted your android phone using a computer. But, if for some reason the tool doesn’t work for you, then use the magisk to root android using TWRP recovery.
Root Android Without PC
While rooting your Android phone using a PC is a popular and successful method, it’s not the only way to achieve root access on your device. If you don’t have a PC or prefer to root your phone without a PC, KingoRoot also offers a one-click rooting method that can be done directly from your phone.
Here are the steps on how to root your android device without a PC using KingoRoot:
- Download and install the KingoRoot APK on your Android device. You can download the APK directly from the KingoRoot website or a third-party app store.
- Once the APK is installed, launch the KingoRoot app.
- Tap the “One Click Root” button.

- Click the “Root” button again to confirm. The rooting process will begin and take a few minutes to complete.

- Once the rooting process is finished, your device will reboot.

Congratulations! You have successfully rooted your Android device without a PC.
What to Do After Rooting Your Android Device
Once your phone is rooted, there are a lot of things that you can do. Out of them, here are some of the things you can do after rooting your android device:
Check If Your Device Is Rooted
The first thing you should do after rooting your device is to check if your device is actually rooted. There are a few different ways to do this, but the easiest way is to use a root checker app. There are many root checker apps available on the Google Play Store. Install one of these apps and open it. If your device is rooted, the app will tell you so.
Backup Your Rooted Phone
Before you start making any changes to your rooted device, it is important to back up your data. This is because rooting your device can sometimes cause problems, and you may need to restore your device to a previous state if something goes wrong. There are a few different ways to back up your rooted device.
One way is to use a third-party backup app, such as Titanium Backup or Helium. Another way is to use the built-in backup feature in your device’s settings.
Manage Root Permissions
Rooting your device gives apps access to the root level of your device’s OS. This can be a security risk, so it is essential to manage root permissions carefully. You can use a root management app like SuperSU or Magisk. A root management app will allow you to grant or deny root permissions to individual apps.
Install Root Apps and Custom ROMs
Now that you have root access, you can install root apps and custom ROMs. There are many root apps and custom firmwares are available for android devices. These apps and ROMs can give you various new features and capabilities.
Here are a few popular root apps:
- AdBlock: Blocks ads in apps and web browsers.
- Greenify: Hibernates apps when you are not using them, which can save battery life.
- Xposed Framework: Allows you to install modules that add new features and functionality to your device.
Here are a few popular custom ROMs:
- LineageOS: A popular ROM based on the Android Open Source Project.
- Pixel Experience: A ROM that is based on the Google Pixel phones.
- Resurrection Remix: A ROM that offers a wide range of customization options.
Tips to Secure a Rooted Phone
While rooting your Android phone unlocks a world of customization and flexibility, it also comes with inherent security risks. With root access, malicious apps can gain complete control over your device, potentially compromising your data and privacy. To safeguard your rooted phone, follow these essential security practices:
Be Cautious with Root Permissions:
Root permissions grant apps extensive control over your device’s system. Be selective about giving root access to apps. Only grant root privileges to trusted apps from reputable sources and deny root access to apps that don’t require it.
Install Custom ROMs from Trusted Sources:
Custom ROMs can provide a fresh look and feel for your phone, along with enhanced performance and features. However, only install custom ROMs from trusted sources, such as XDA Developers or CyanogenMod. Avoid ROMs from unknown sources, as they may contain malware or vulnerabilities. Also, install only the stable custom rom and recovery to avoid unnecessary bugs.
Use a Custom Recovery:
A custom recovery like TWRP offers advanced features for managing your rooted phone, including backing up and restoring your system, installing custom ROMs, and troubleshooting issues. Also, before making any significant changes to your device, always take a full android backup so in case anything happens, you can revert to the previous state.
Avoid Installing Apps from Unknown Sources:
Only install apps from trusted sources like the Google Play Store or reputable third-party app stores. Avoid downloading apps from unofficial websites or app markets, as these may contain malware or spyware.
Keep Your Phone Updated:
Regularly update your phone’s android version and security patches. These updates often include security enhancements and bug fixes to address vulnerabilities and protect your device from newly discovered threats.
Conclusion
Rooting an android device is a decision that should not be taken lightly. Carefully weigh the benefits against the risks before proceeding. If you are comfortable with the potential risks and are experienced with flashing ROMs and modifying software, then rooting may be a worthwhile option. However, if you are not satisfied with these risks or lack experience, then rooting may not be the right choice for you.
In conclusion, rooting an Android phone offers a range of benefits, including enhanced performance, customization options, and access to advanced features. However, it also comes with potential risks, such as security vulnerabilities, warranty voiding, bricking, and compatibility issues. Carefully consider these factors before deciding whether or not to root your device.